Syntax
PTP P_value, T_value, C_value |
Define a PT point via immediate values |
PTP P_var, T_var, C_value |
Define a PT point via TML variables |
| Operands | P_value – 32-bit long integer immediate value: PT point position |
T_value – 16-bit unsigned integer immediate value: PT point time
C_value – 7-bit integer immediate value, PVT point integrity counter
P_var – long variable, contains the PT point position
T_var – integer variable, contains the PVT point time
![]()
Binary code
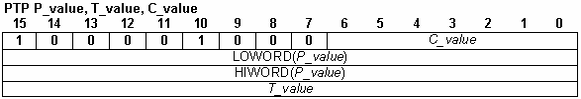
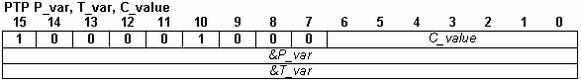
| Description | Defines a PT point. The PT position and time values may be provided either as immediate values or via the values of 2 TML variables. |
A PT point also includes a 7-bit integrity counter. The host must increment by one the integrity counter each time when it sends a new PT point. If the integrity counter error checking is activated, every time when the drive/motor receives a new PT point, it compares its internally computed integrity counter value with the one sent with the PTP command. The PT point is accepted only if the two values are equal. If the values of the two integrity counters do not match, the integrity check error is triggered, the drive/motor sends the PVTSTS to the host with PVTSTS.12 =1 and the PT point received is discarded. Each time a PT point is accepted, the drive/motor automatically increments its internal integrity counter.
Example
SETPT 0xCF00; //Clear PT buffer
MODE PT; // Set PT Mode
TUM1; //Start from actual value of position reference
CPR;
PTP 2000L, 2000U, 0; //PT(1[rot], 2[s])
UPD; //Execute immediate
PTP 6000L, 500U, 0; //PT(4[rot],2.5[s])
PTP -2000L, 500U, 0; //PT(3[rot],3[s])
!MC; WAIT!; //wait for completion